[toc]
We use cheques for many different transactions. Even though lots of newer payment methods have come up in the last few years, cheques are still used very often.
Where is the cheque number?
There are many times when we need to note down the cheque number. So what is a cheque number? To put very simply, every cheque has a unique number that helps to identify it. Let’s understand a cheque format.

- The cheque number is a 6 digit number and is always written at the bottom left-hand corner of the cheque. For the above cheque, the cheque number is ‘950020’.
- After the cheque number comes the MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) code. The 9 digits of the MICR code indicate the bank and the branch that issued the cheque. The first 3 digits are the city code, the next three digits are the bank code, and the last three digits are the branch code. For the above cheque, the MICR code is ‘695002032’.
- The 6 digits after the MICR code are a portion of the account number. For the above cheque, it is ‘002860’.
- And the last two digits at the bottom are the transaction ID. They indicate whether the cheque is a local cheque, or payable at par cheque. A local cheque can be cashed only at the issuing bank, and a payable at par cheque can be cashed at any branch of the issuing bank. However, post the establishment of the Core Banking System at all banks, most cheques are payable at par cheques only. For the above cheque, the transaction ID is ’31’.
- All of the above numbers are written in a special magnetic ink so that they can read with a Magnetic Character Ink Reader.
- The cheque format in India is generally the same for all banks.
How to check the status of a deposited cheque?
To track the status of a cheque that you have deposited in your account, you can do either of the following:
- Get your passbook updated. If the cheque has got cleared, your account will be credited.
- Check your balance and account statement using e-banking.
- Check your account balance at an ATM.
- If you have registered your mobile number, you might get an SMS when the cheque amount is credited to your account.
- Go the bank, and ask at the counter.
Let’s discuss the different types of cheques:
What is a Personal Cheque?
- It is cheque drawn on a personal account.
- It is signed by the person whose account it is drawn on.
- A personal cheque is generally used for transactions of a small amount.
- If there aren’t enough funds in the account to cover the amount of the cheque, the check doesn’t clear. Hence there is a certain level of risk in accepting personal checks from unknown people.
What is a Cashier’s Cheque?
- It is drawn on the bank’s own funds, guaranteed by the bank, and signed by a cashier.
- It is also called guaranteed funds because the bank is responsible for paying the amount.
- Cashier’s cheques are commonly used in real estate transactions.
- You can buy them from the bank for a fee.
- However, be careful about forged cashier’s cheques and fraudulent schemes. Cashier’s cheques usually clear in a day. But if there is some fraud, the bank may take weeks to discover it. If you have withdrawn funds after depositing a fraudulent cashier’s cheque, you are legally liable for the funds withdrawn.
- Cashier’s cheques are also referred to as bank cheques or official cheques.
What is a Bearer Cheque?
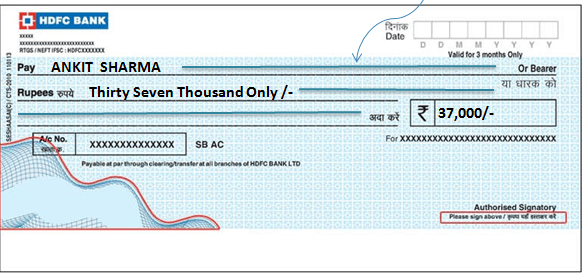
- In such a cheque, the words “or bearer” appearing on the face of the cheque are not cancelled.
- It is payable to the person specified on the cheque or to anyone else who presents it to the bank.
- Hence, such cheques are risky, because if they are lost, anyone who finds the cheque can collect the payment from the bank.
What is an Order Cheque?

- When you cancel the word “bearer” appearing on the face of the cheque, and in its place write “or order”, it is called an order cheque.
- It is payable to the person specified on the cheque or to anyone else to whom it is endorsed/transferred.
What is a Crossed Cheque?
- A crossed cheque has two parallel lines drawn on the face of the cheque.
- And you may or may not add additional words like “& CO.” or “Account Payee” or “Not Negotiable”.
- Such a cheque cannot be en-cashed at the cash counter of a bank.
- So it has to only be credited to the payee’s account.
What is an Uncrossed/Open Cheque?
- It is simply a cheque which is not crossed.
- You can obtain the payment of such a cheque at the bank counter.
- It can be either a bearer cheque or an order cheque.
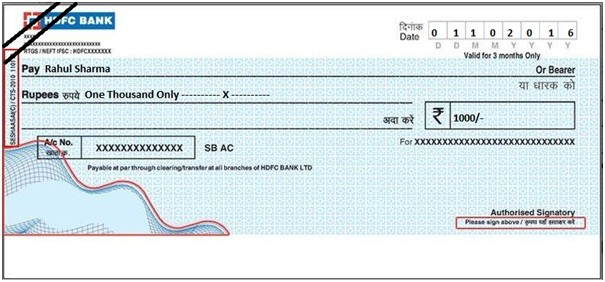
What is an Anti-Dated Cheque?
- If the cheque bears an earlier date than the date on which it is presented to the bank, it is called an anti-dated cheque.
- It is valid upto 3 months from the date of the cheque.
What is a Post-Dated Cheque?
- If the date of the cheque is yet to come (it bears a future date), it is called a post-dated cheque.
- The bank does not honour it before the date of the cheque.
What is a Stale Cheque?
- It is a cheque that is presented for payment after 3 months of the date of the cheque.
- The bank does not honour stale cheques.
The above information will hopefully help you to understand cheque number SBI, cheque number ICICI bank, cheque number HDFC bank, cheque number Axis bank, etc. To read about Account Payee Crossed Cheques and Bearer Cheques, please click here.
March 6, 2019 4:33 pm
cheque no floating point values accept or not
March 6, 2019 4:46 pm
cheque no floating point values accept or not and cheque no accept only 6 digits are not