New Income Tax Return Forms AY 2017-18 are notified by Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT). To make ITR filing easy some changes are made in the ITR forms, the format, however, is similar to the previous year. You can easily file an Income Tax Return electronically. The last date to file an ITR for the financial year 2016-17 is 31st March 2017. Below is the eligibility criterion for filling ITR in the paper for when filing a return in ITR-1 (Sahaj) or ITR-4 (Sugam):
- Individuals who are 80 years or above in age at any time during the past year are eligible to file an ITR on paper.
- Individuals or Hindu Undivided Family having an income less than 5 Lakh rupees are eligible to file ITR on paper. These individuals should not have claimed any reimbursement in the return of income.
[toc]
What is AY & FY?
Financial Year (FY) refers to the year in which an individual has earned an income. On the other hand, the Assessment Year (AY) is that in which an individual file a return. For example, Suppose you are filing a return for the income earned between 1st April 2016 and 31st March 2017. In this case, the Financial Year (FY) will be 2016-17 and Assessment Year (AY) will be 2017-18. The last date to file an Income Tax Return for Financial Year 2016-17 is 31st March 2017.
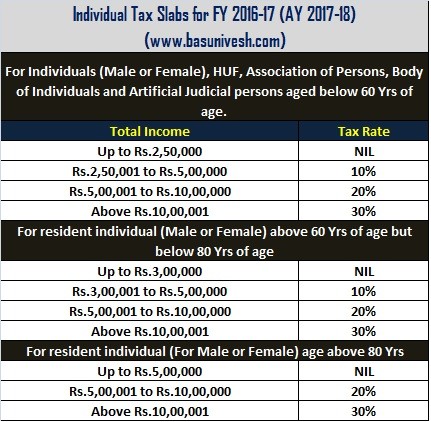
Income Tax Slabs for AY 2017-18 (FY 2016-17):
Let us first understand the taxation for FY 2016-17 or AY 2017-18 then we will go to understanding the Income Tax Return Forms AY 2017-18:
Below is the chart for Capital Gain Tax for FY 2016-17 (AY 217-18)
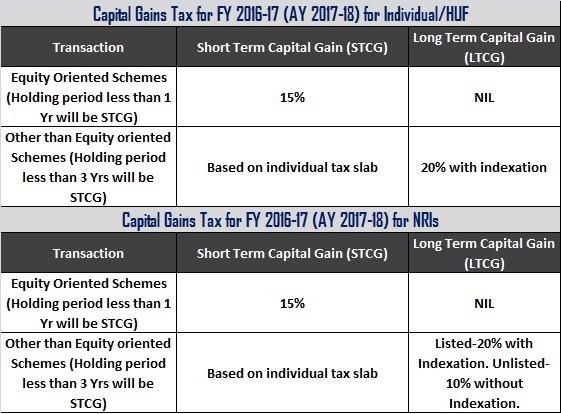
The above charts might have given you an idea of in which tax slab you fall and what is your tax liability.
Income Tax Return Forms AY 2017-18 (FY 2016-17) – Which form to use?
Below are the new changes made in the Income Tax Return Forms AY 2017-18 (FY 2016-17):
- A new single page ITR-1 (Sahaj) form is introduced. Around 2 crore taxpayers, who can file ITR, will benefit from this initiative from the government of India.
- Income Tax Return Forms AY 2017-18 (FY 2016-17) are reduced from nine to seven forms.
- The existing Income Tax Return Forms ITR-2, 2A, and 3 are converted to a single ITR-2 form.
- Existing ITR-4 and ITR-4S (Sugam) Forms are renumbered as ITR-3 and ITR-4 (Sugam) respectively.
- The pattern of ITR is same.
- Sahaj and Sugam forms can be used to file a return.
Some more changes made in ITR-1 Form:
- Only these people can file income tax return on paper: (i) Individual who are 80 years or above in age at any time of the past year, or (ii) an individual or Hindu Undivided Family with an income between 5 lakh or less and have not claimed for a reimbursement in the return of income.
- It has become mandatory to link your Aadhaar card for any ITR filing in future.
- Now, it is important to quote your Aadhaar card number while filing an ITR return.
Two new columns added to ITR-1 Form:
- A new column is introduced in the ITR forms to report a cash deposit of more than INR 2 lakhs by taxpayers in their respective bank accounts during the demonetization period i.e. 9th November 2016 to 30th December 2016.
- ITR forms get a new column under schedule VI-A deductions which can be used to claim interest on home loan under 80EE section.
ITR 1 (Sahaj) Form for Assessment Year 2017-18:
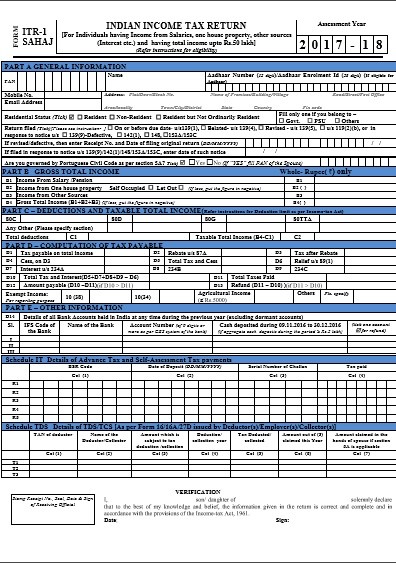
This form is used to file a return on the income generated during FY 2016-17 (AY 2017-18).
An individual can use this form in the following cases:
- When the income generated is from salary or pension;
- The income is from One House Property (excluding cases where loss brought forward from previous years);
- Income is generated from other sources, which excludes income from lottery, race horses, and income taxable under Section 115 BBDA;
- Income from minor child or spouse etc if clubbed with assessee, then ITR can be filed only if it falls in any of the above categories.
An individual cannot use the above form in these cases:
- If the total income for the Assessment Year 2017-18 exceeds Rs 50 lakhs;
- Income from more than one house property;
- Winnings from lottery or income from race horses;
- The earned income is taxable under section 115BBDA;
- Income nature referred to in section 115BBE;
- A person has earned an income under the head “Capital Gains”;
- Agricultural income in excess of Rs 5,000;
- Income from Business or Profession;
- Loss under the head “Income from other sources”;
- Person claiming relief under section 90 and 91;
- An Indian resident who has an asset in a foreign country or is a signing authority in a bank account outside India;
- Any resident having income from any source outside India.
ITR-2 Form for Assessment Year 2017-18:
An individual can use this form in the following cases:
- An individual or a Hindu Undivided Family.
- Salary or Pension are the main income sources.
- Multiple house property generates income.
- Income from Capital Gains.
- A person generates income from various other sources like winnings from lottery and income from race horses.
- The person has an asset in a foreign country or an income from a source outside India.
- Agricultural income of more than Rs 5,000;
- Income from the spouse, minor child, etc., if clubbed with the assessee, then ITR-2 Form can be filed if it falls in any of the above categories.
An individual cannot use this form in the following cases:
- Income from business or profession.
ITR-3 Form for Assessment Year 2017-18:
- ITR-4 Form is now ITR-3.
- Individuals and Hindu Undivided Families.
- You can use this form if you have an income source from proprietary business, profession or from a partnership firm.
- Income from multiple house properties, salary, capital gains, lottery winnings, business, horse race or professional income.
ITR-4S (Sugam) Form for Assessment Year 2017-18:
An individual can use this form in the following cases:
- An individual or Hindu Undivided Family or a partnership firm.
- Business income computed as per the special provisions referred in sections 44AD and 44AE of the Act for computation of business income.
- Income from a profession computed as per special provisions referred to in sections 44ADA.
- Salary or Pension are the main income sources.
- Income from other sources, excluding the income generated from lottery winning and race horses.
An individual cannot use this form in the following cases:
- One house property as the major income source.
- Winnings from lottery or income from race horses have earned an income.
- Income under the head “Capital Gains”, e.g. short-term capital gains or long-term capital gains from the sale of the house, plot or shares etc.
- The earned income is taxable under the section 115BBDA.
- Income of nature referred to in section 115BBE.
- Agricultural Income in excess of Rs 5,000.
- Speculative Business and other special incomes.
- The income earned from an agency business or income in the nature of commission or brokerage.
- A person claiming relief of foreign tax paid under section 90, 90A or 91.
- Any resident having an asset (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India or signing authority in any account located outside India.
- Any resident having an income from any source outside India.
Leave a Reply